What causes sores on the penis?
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/326583.php
A sore is a painful bump or wound. Sores can appear on any part of the skin, including on the penis. Penis sores often result from a sexually transmitted infection or a skin condition.
While some penis sores will clear up on their own, many require treatment to prevent symptoms from getting worse, complications, and transmission to others.
In this article, we list 12 potential causes of penis sores and the treatments available for each one.
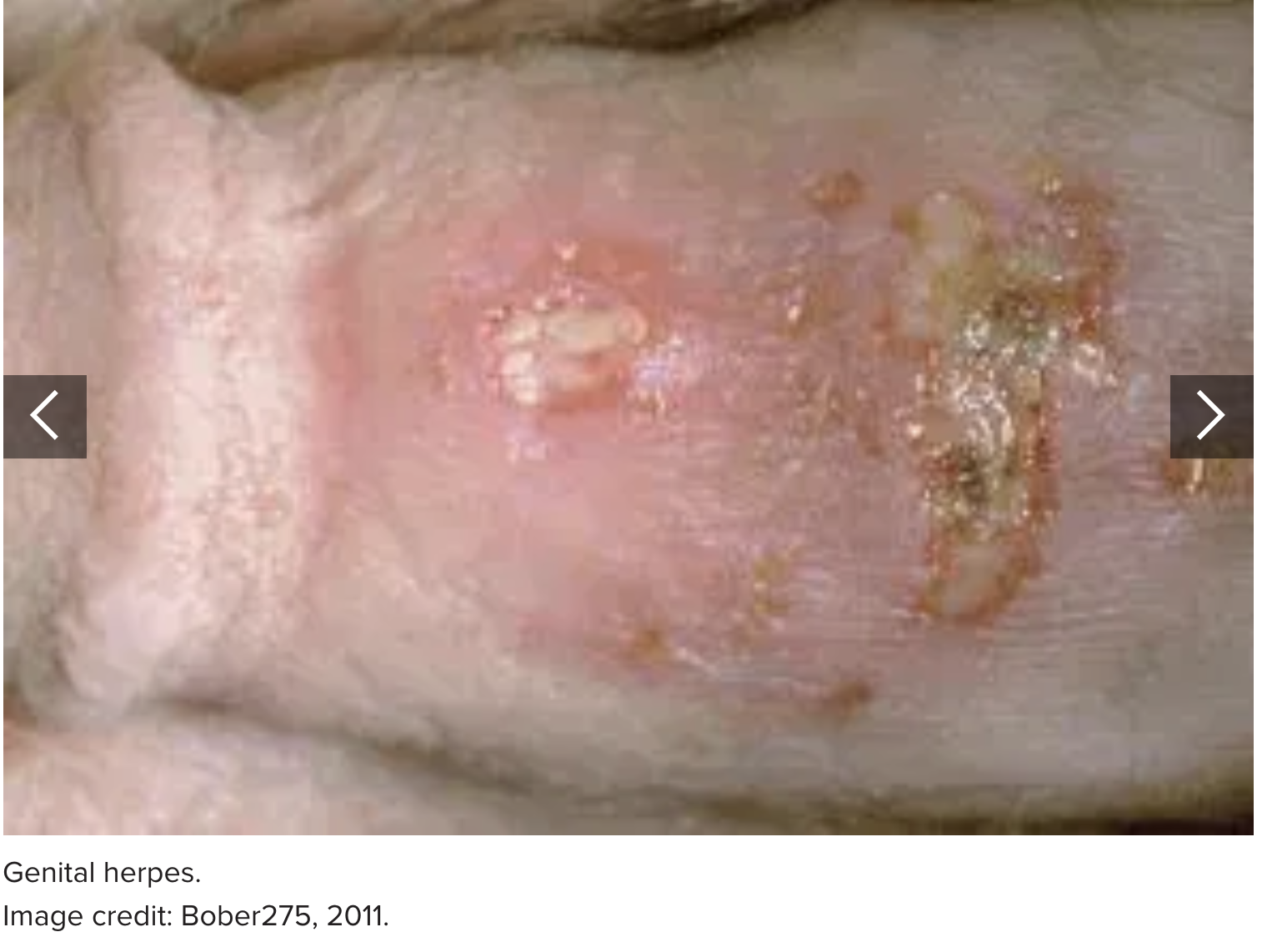
1. Genital herpes
Genital herpes is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) that passes from one person to another during sexual activity. In the United States, more than 1 in every 6 people aged 14–49 have genital herpes.
The herpes simplex virus causes genital herpes. Its symptoms can include painful, itchy, fluid-filled, blistering sores on the penis and other parts of the genitals. When these blisters burst, they can leave scars.
Treatment
There is no cure for herpes, but antiviral medications can help prevent or treat outbreaks.
Individuals should avoid sexual activity until the sores go away. People should also refrain from touching the sores, as this may cause them to spread the virus to other areas.
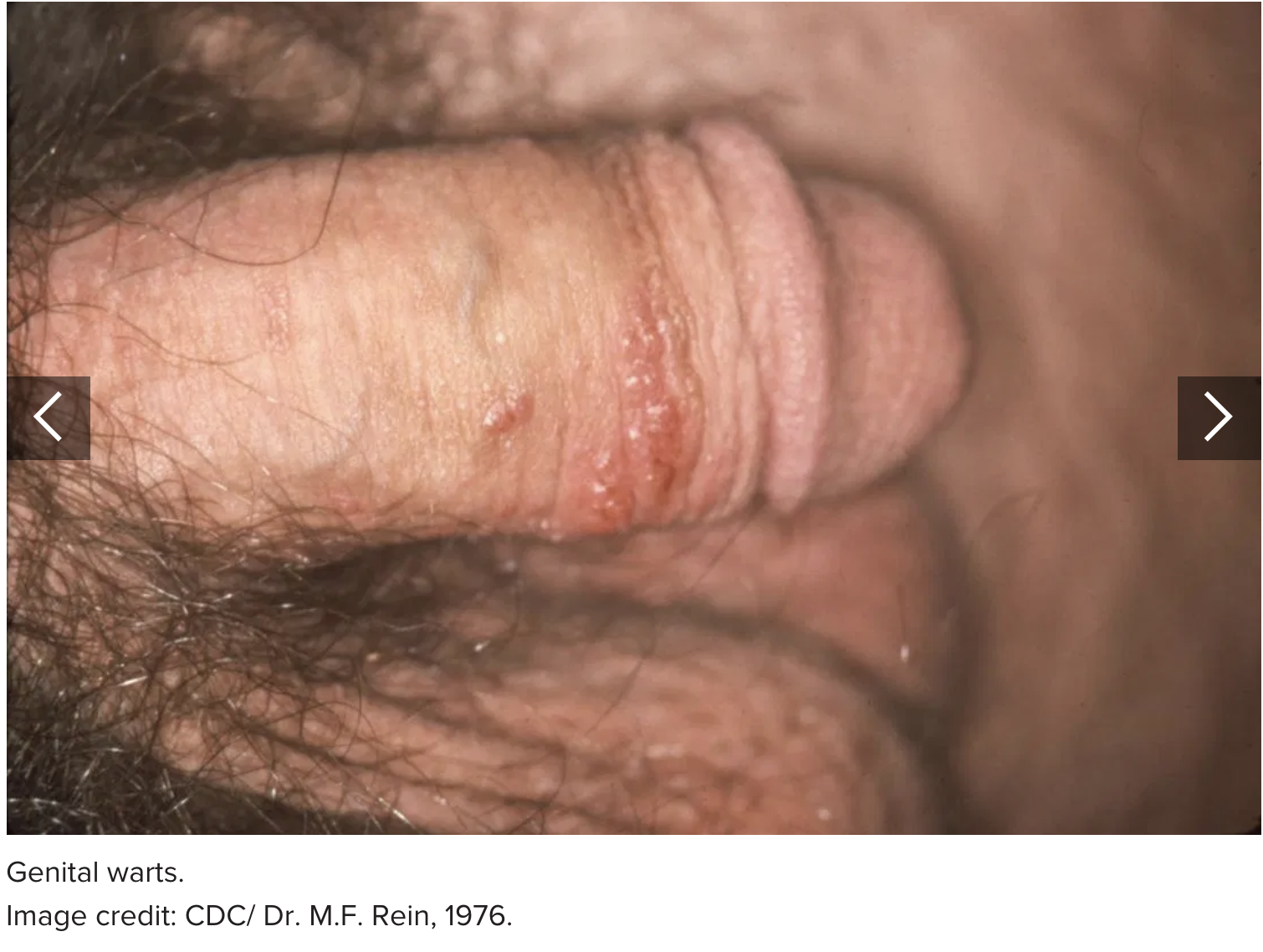
2. Genital warts
Genital warts are another type of viral STI, caused by the human papillomavirus. They appear on the penis as small, bumpy, sometimes stalky, cauliflower-like growths. Genital warts can cause itching and discomfort.
Approximately 1% of sexually active people in the U.S. have genital warts at any given time.
Treatment
If the warts do not cause pain and discomfort, then no treatment is necessary. For up to 1 in 3 people with the condition, the warts will go away on their own within 2 years.
To remove the warts, a doctor can freeze them off, perform laser surgery, or prescribe a topical medication to destroy the warts. These treatments do not kill the virus that causes the warts, however, so they may return in the future.
Individuals should avoid sex for at least 2 weeks after the warts have gone away. It is still possible to spread the virus to others after this time, so it is important to use barrier protection when having sex.
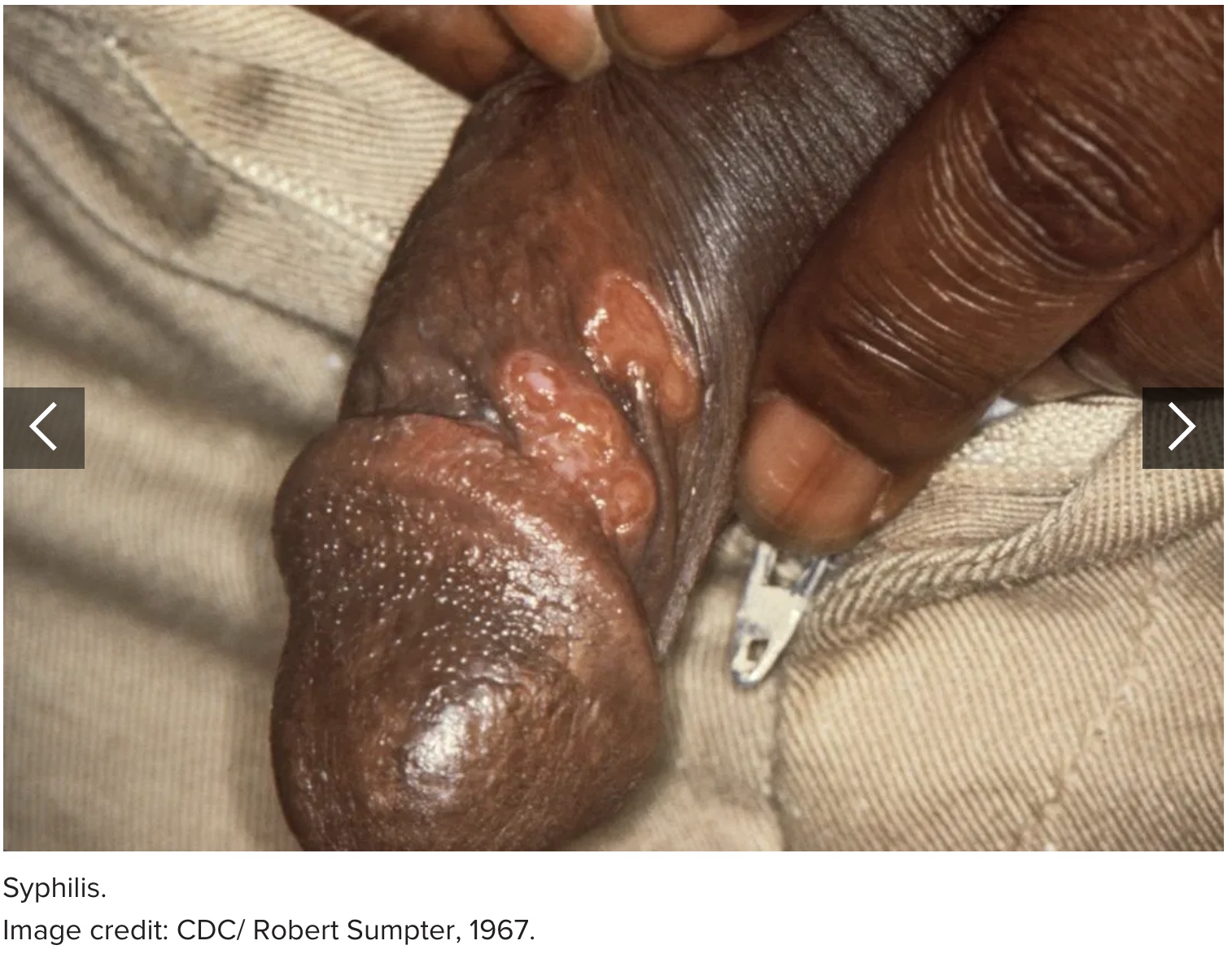
 3. Syphilis
3. Syphilis
Syphilis is a severe bacterial infection and another type of STI.
In the early stages of infection, syphilis usually causes a hard, painless, red sore on the penis. This sore lasts for 3–6 weeks.
Untreated, syphilis can lead to:
cardiovascular problems
dementia
hearing or vision loss
increased risk of HIV infection
meningitis
pregnancy, childbirth, and fetal complications
stroke
Treatment
If a person suspects syphilis, they must seek medical attention as early as possible to prevent the infection from progressing and causing severe, lasting health complications.
A penicillin injection is the main form of treatment for syphilis.
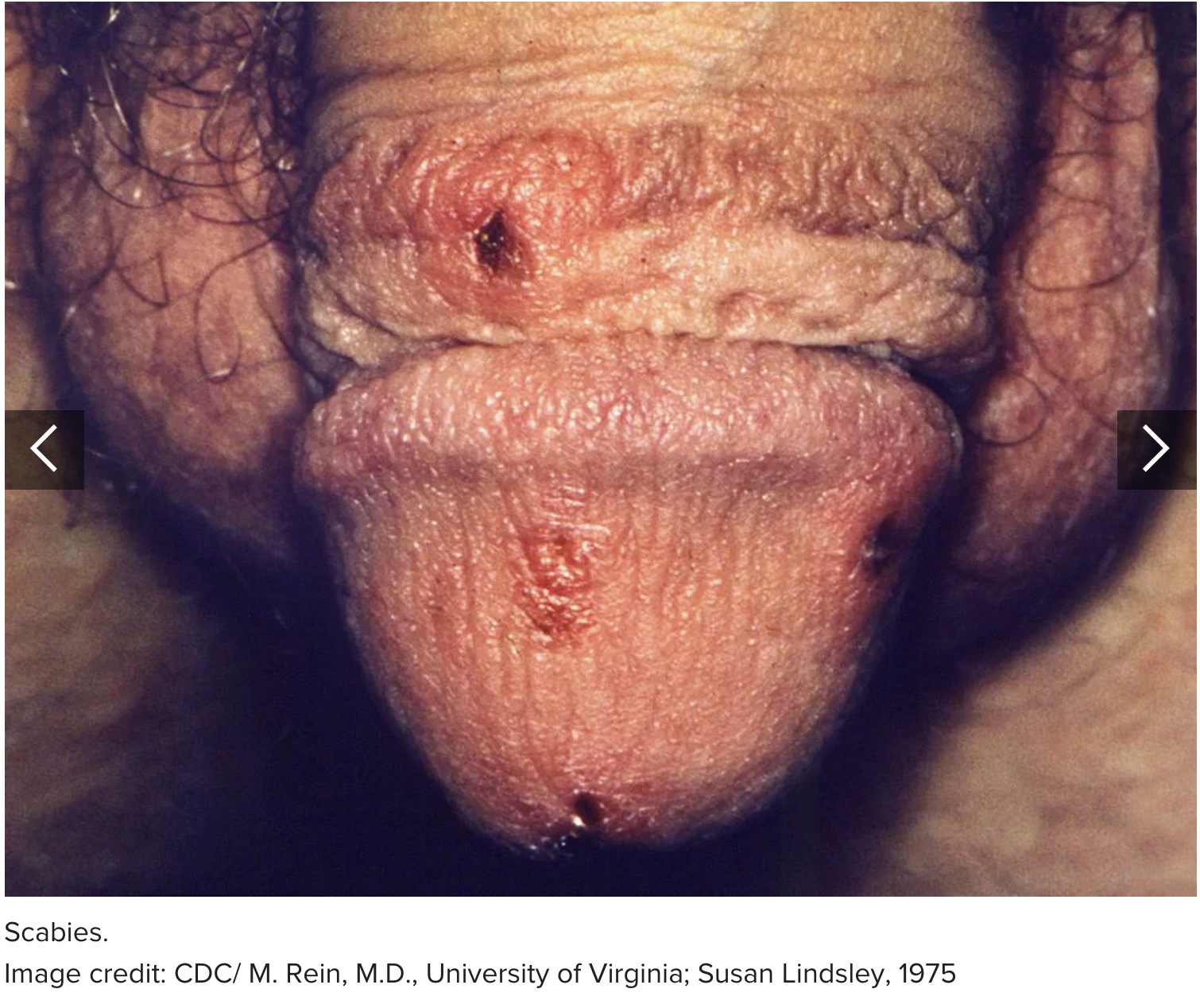
 4. Scabies
4. Scabies
Scabies is a contagious skin condition that can affect many parts of the body, including the penis.
People get scabies when the Sarcoptes scabiei mite burrows into the skin. Sexual contact increases the risk of scabies in the penis.
Scabies causes tiny blisters or sores on the skin that are extremely itchy, especially at night. These sores typically occur in thin, irregular lines showing the path of the mite under the skin.
After an infestation occurs, a person who has never had scabies before may not develop symptoms until after 4–6 weeks. Symptoms typically show up within 1–4 days in cases of a second or subsequent infestation.
Treatment
Prescription creams and lotions are the first line of treatment for scabies. If these do not work, a doctor may prescribe oral medications.
Cold compresses and antihistamines can relieve itching until the scabicide medication takes effect.
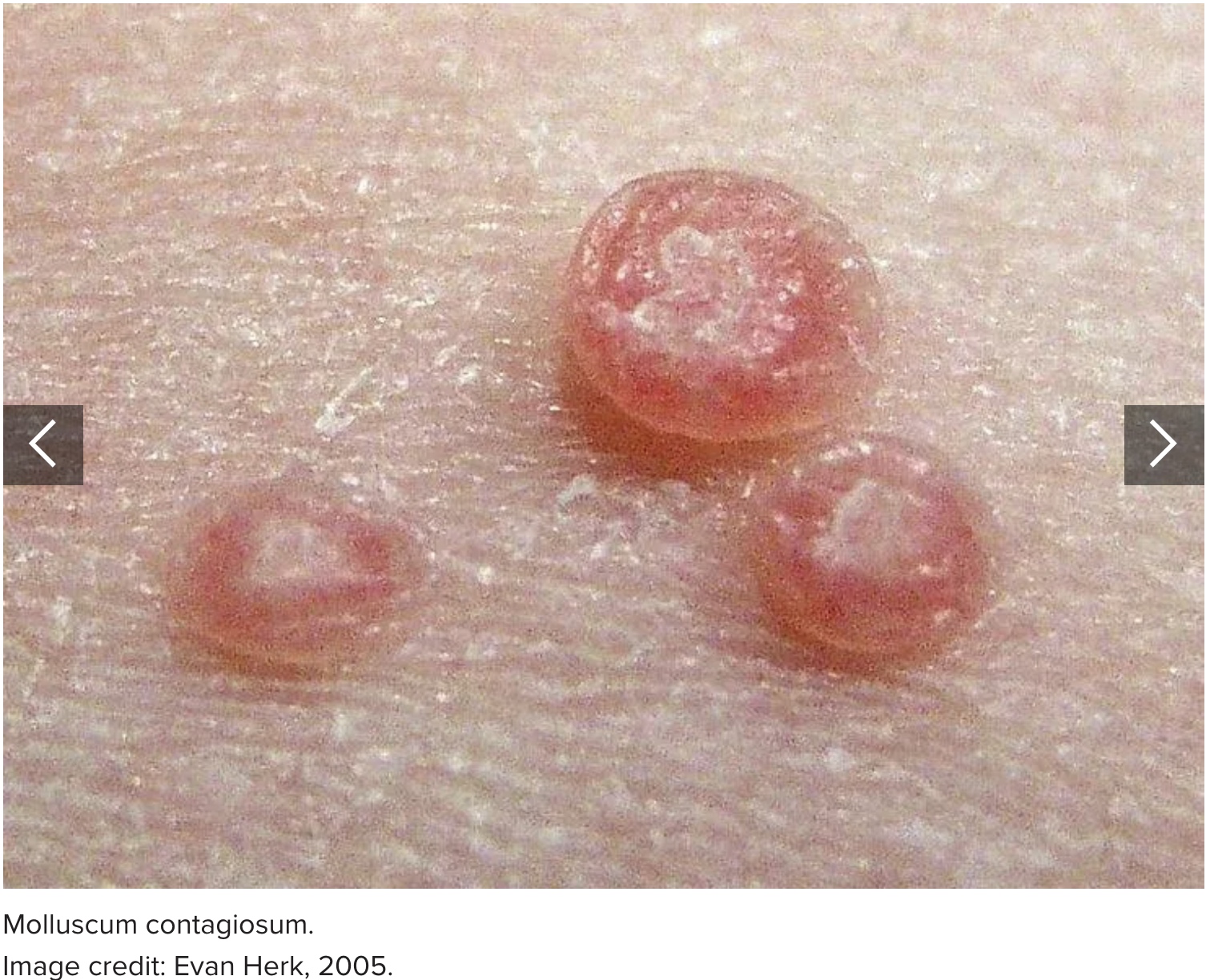
 5. Molluscum contagiosum
5. Molluscum contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum is a viral skin infection. Anyone can catch molluscum contagiosum from direct contact with others or from sharing towels or personal items. Sexual contact can cause it to develop on the penis.
Symptoms include itchy, round, raised, pink or flesh-colored sores on the penis. These can occur alone or in clusters.
Many cases clear up without treatment within 12–18 months. While sores are present, people can transmit molluscum contagiosum to others.
Treatment
To remove the sores and to avoid transmitting the infection to others, doctors recommend:
topical creams or lotions
surgical removal of the lesions with a curette, which is a small hooked tool
cryotherapy
laser surgery
 6. Chancroid
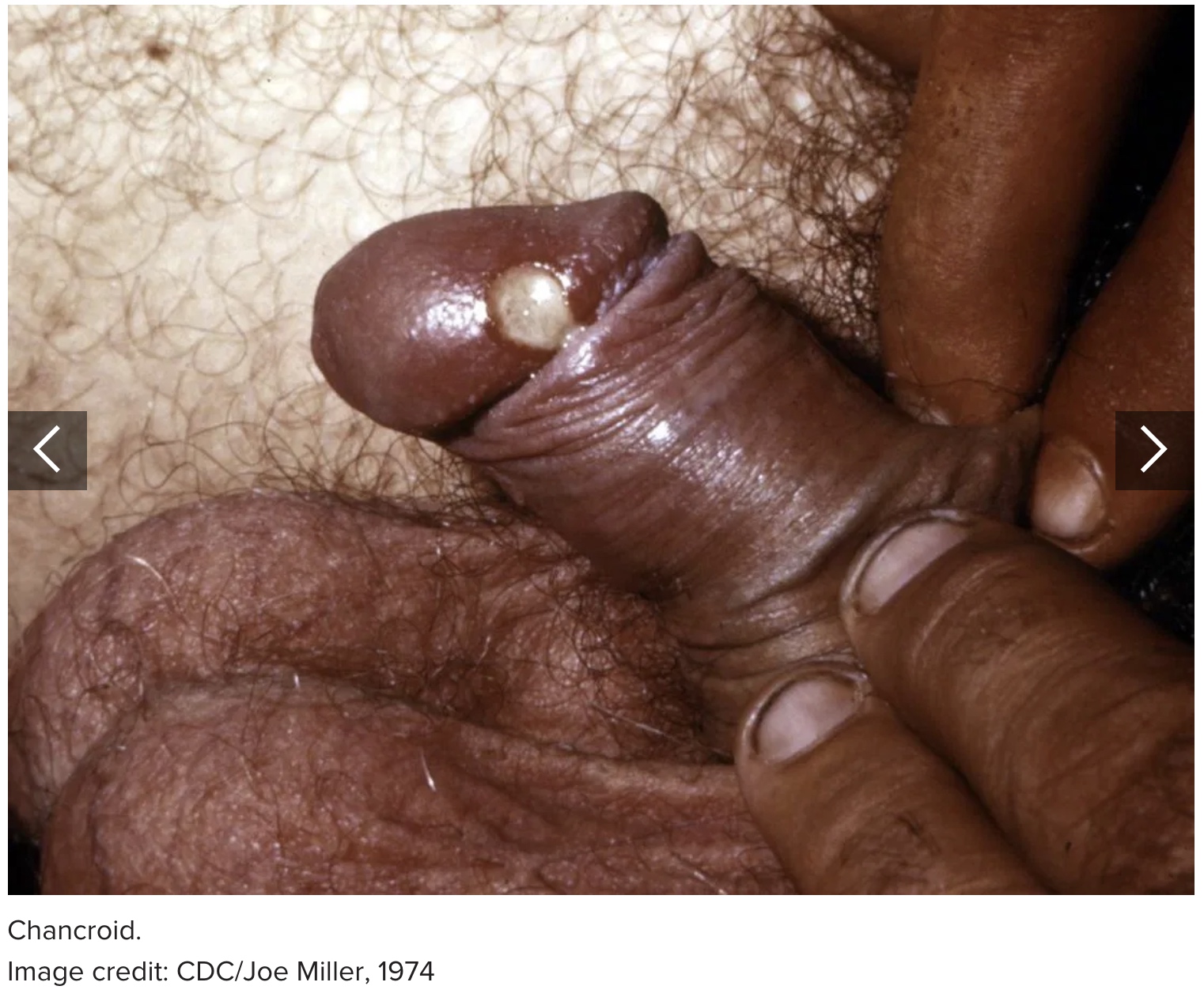
6. Chancroid
Chancroid is a bacterial infection that the Haemophilus ducreyi bacterium can cause. It spreads from one person to another through sex without barrier protection.
The infection causes small, red, raised sores to form on the penis. These are itchy and painful, and they ooze blood or other fluid when they later open and become ulcerative.
Other symptoms include pain during sexual activity or urination, and swelling in the groin.
Treatment
As with other bacterial infections, the main treatment for chancroid is antibiotic medication. Treatment can cure the infection and prevent it from spreading to others.
Chancroid is a risk factor for HIV infection.
 7. Granuloma inguinale
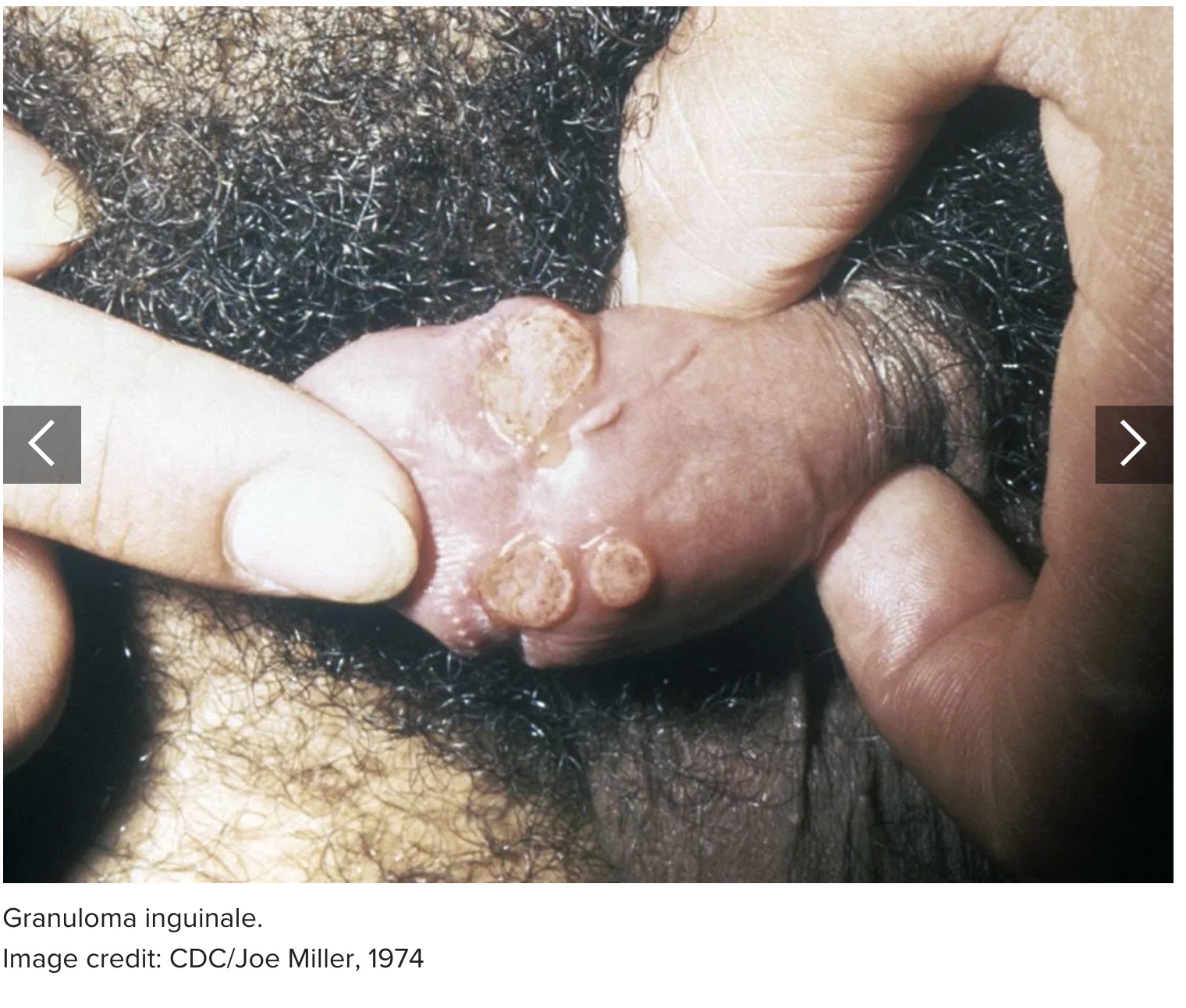
7. Granuloma inguinale
Granuloma inguinale is a bacterial STI that causes ulcers to form on the genitals and anus. It is rare in the U.S., but common in some developing regions.
In the beginning, the infection causes small, painless bumps. Over time, these sores slowly develop into deepening ulcers that bleed.
Treatment
Antibiotics treat the infection and reduce the risk of scarring.
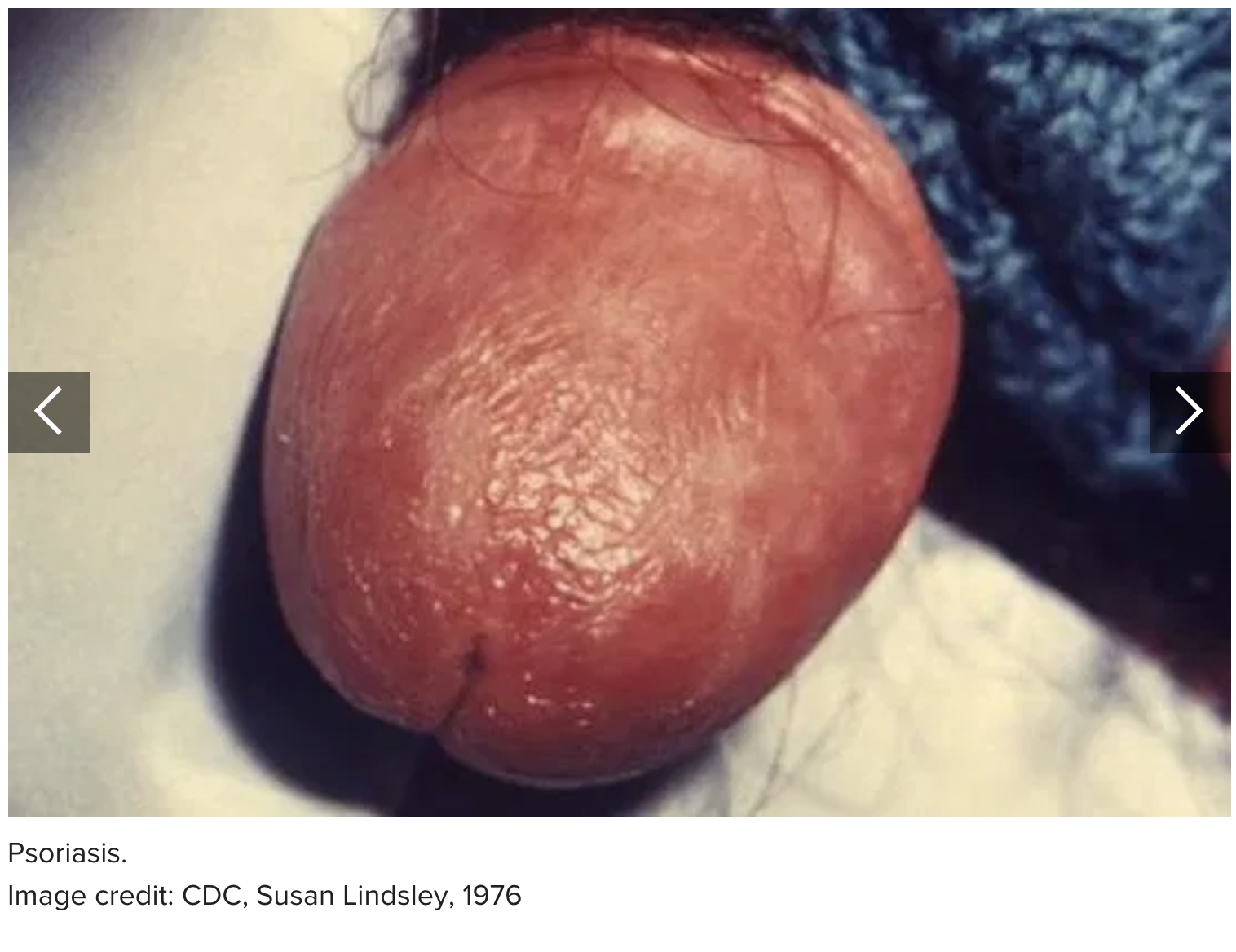
8. Psoriasis
Psoriasis is an autoimmune skin condition that causes red, scaly patches of skin. On the penis and genitals, it can cause:
a red rash with silvery scales
dry, cracking skin that may bleed
itching, pain, and discomfort
Symptoms vary from one person to another. In some, it may appear as just a few spots, while others experience a widespread rash.
Treatment
There is no cure for psoriasis, but treatment aims to keep symptoms under control. Medical treatments include:
topical creams and ointments
oral medications
injected medications
UV light therapy
Lifestyle changes and home remedies can relieve discomfort. These include cool compresses, moisturizing lotions, and stress management.
 9. Atopic dermatitis
9. Atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis, or eczema, is a chronic skin condition. It can affect many body parts, including the penis.
An eczema rash causes red, flaky bumps that itch. The bumps may blister and burst before forming a scab.
Eczema occurs in people who have a gene variant that affects their skin's ability to protect against irritants and allergens. Eczema rashes on the penis may result from contact with scented cleansing products, laundry detergents, or from chafing from clothing.
Treatment
Mild eczema may respond to the following home remedies:
cool compresses
warm oatmeal baths
loose clothing
moisturizing with an unscented lotion
If these do not work, a doctor may prescribe oral or injectable medications or topical creams.
Learn more about home remedies for eczema here.
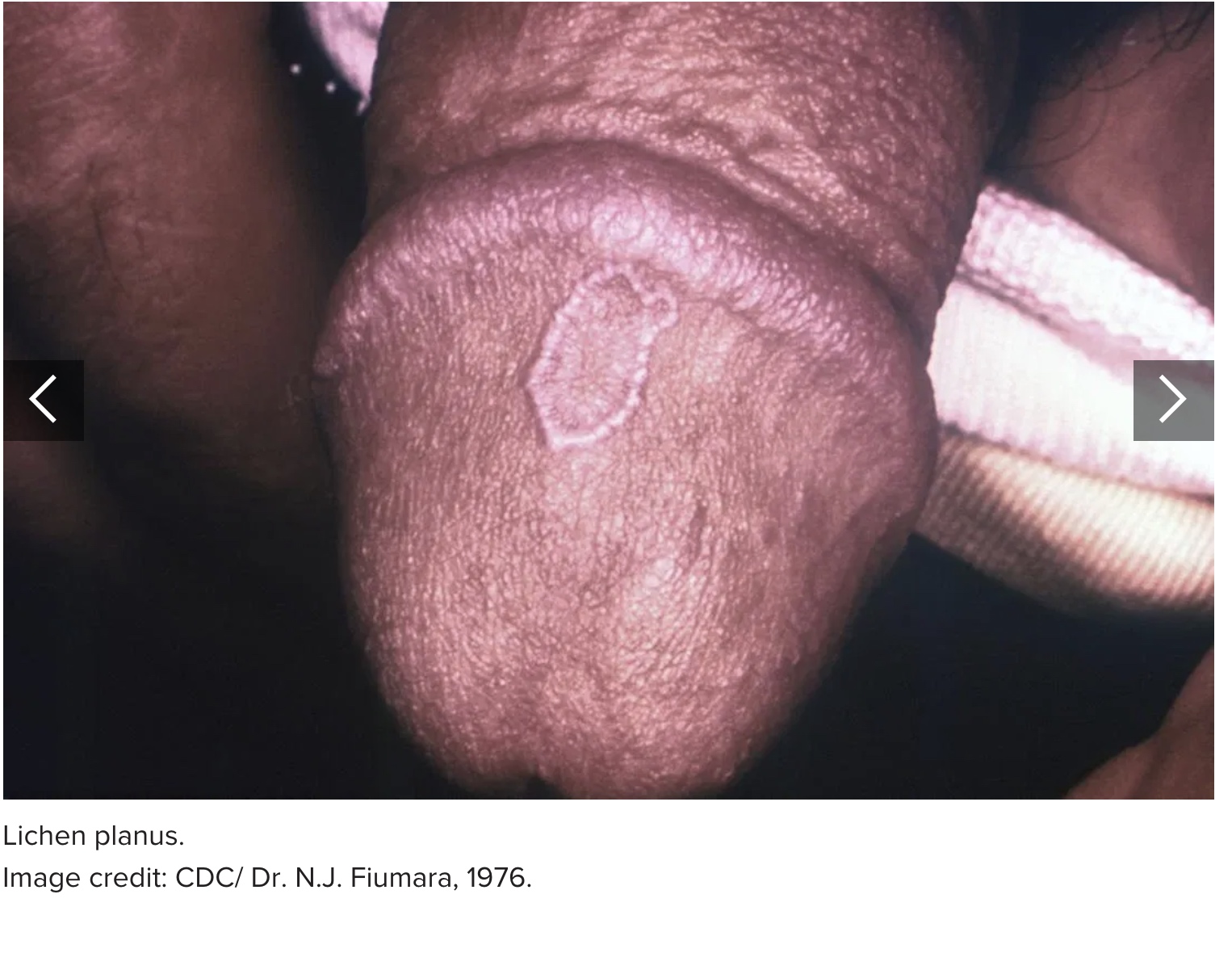
 10. Lichen planus
10. Lichen planus
Lichen planus is another autoimmune skin condition. It causes an itchy rash characterized by flat, purple-red bumps. The rash may develop on the penis, inner arms, wrists, ankles, or other body parts.
These sores may form blisters that ooze and crust over. Painful, white sores that look like lace may also develop in the mouth.
Treatment
Treatment for mild cases of lichen planus includes oatmeal baths, cool compresses, and over-the-counter (OTC) hydrocortisone creams.
If these options do not work, a doctor may prescribe medication.
 11. Diabetes ulcers
11. Diabetes ulcers
Diabetes ulcers typically appear on the feet. However, at least one case report describes penile ulcers as a result of diabetes. In this case, treatment involved antifungal cream and medication to control blood sugar levels.
More common symptoms of diabetes mellitus include:
slow healing sores on the skin
frequent skin infections
increased thirst and urination
extreme hunger
fatigue and irritability
blurred vision
Treatment
Diabetes treatment varies from one person to another. Options include medication, a balanced diet, physical activity, and other lifestyle changes.
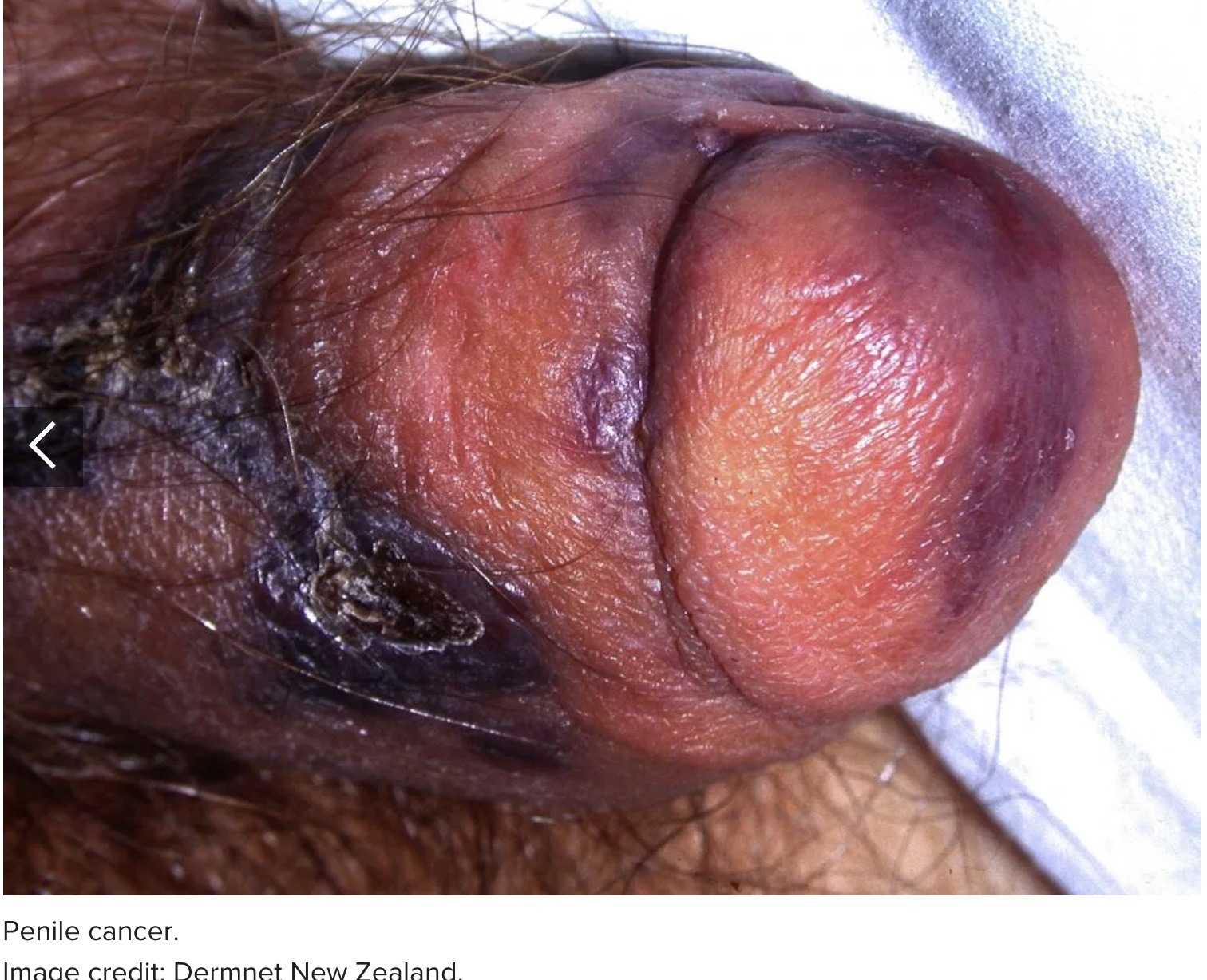
12. Penile cancer
Penile cancer is a rare form of cancer. Typically, the first symptom is a change in the skin of the penis, such as:
a lump or small, crusty sore or ulcer that may bleed
changes in skin color
thickening of the skin
a rash under the foreskin
odorous discharge or bleeding under the foreskin
flat growths
Treatment
Penile cancer requires prompt treatment to stop it from progressing. A doctor may recommend one of the following options:
surgical removal of the foreskin or cancerous tissue
chemotherapy
radiation therapy
 Outlook
Outlook
The outlook for people with penis sores depends on the underlying cause. Typically, penis sores occur due to a STI or chronic skin condition. It is important to avoid sexual activity until a doctor determines the precise cause of the sores.
Seek prompt medical attention if other symptoms accompany the sore, such as:
painful urination or ejaculation
unusual discharge from the penis or the sores
fever or chills
fatigue or a general feeling of illness
unexplained weight loss
The earlier a person seeks treatment, the better the outcome.